In an era where climate change and environmental degradation are pressing global challenges, the need for sustainable solutions has never been more urgent. Renewable energy sources are at the forefront of this movement, offering a way to power our lives without depleting finite resources or harming the planet. Whether you’re an individual looking to reduce your carbon footprint or a business aiming to cut costs and enhance your green credentials, understanding guide to renewable energy sources is essential. This article serves as a comprehensive guide to renewable energy sources, breaking down the key types, their benefits, and practical steps to integrate them into everyday life. By the end of this guide to renewable energy sources, you’ll have the knowledge to make informed decisions and contribute to a cleaner, healthier world.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Renewable Energy
Renewable energy refers to energy derived from natural processes that are continuously replenished, such as sunlight, wind, rain, and geothermal heat. Unlike fossil fuels, which take millions of years to form and release harmful greenhouse gases when burned, renewable energy sources are abundant and environmentally friendly. The transition from traditional energy systems to renewable energy sources is not just a trend—it’s a necessity. With the world’s population growing and energy demand increasing, renewable energy provides a sustainable alternative that reduces reliance on non-renewable resources.
The guide to renewable energy sources is designed to help readers navigate the complexities of this field. It starts by explaining the fundamental principles of renewable energy, followed by an in-depth look at the most common types. Each section will highlight the unique characteristics, advantages, and challenges of different renewable energy sources. This approach ensures that readers can choose the most suitable options for their needs, whether they’re interested in residential applications, industrial uses, or large-scale energy production.
Types of Renewable Energy Sources
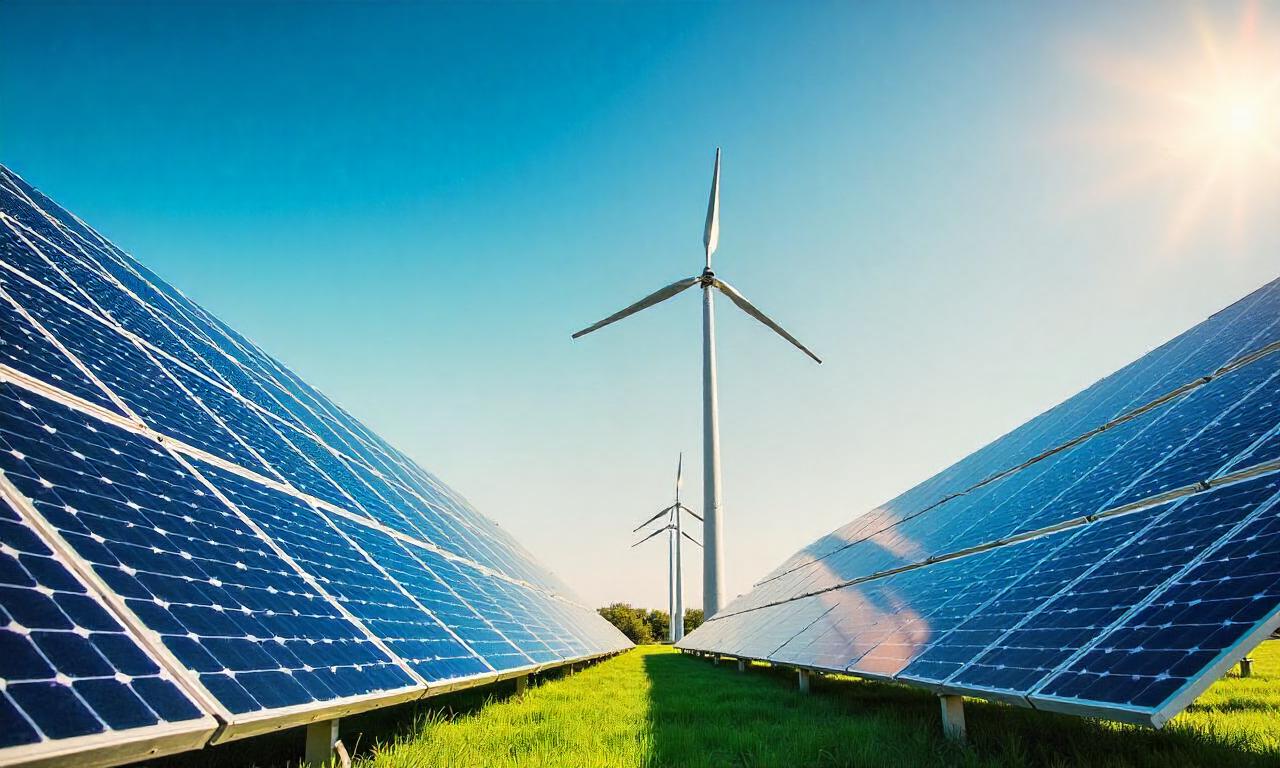
There are several renewable energy sources available today, each with its own strengths and applications. The five most prominent include solar energy, wind energy, hydropower, geothermal energy, and biomass energy. Let’s explore each of these in detail to understand how they contribute to a sustainable energy future.
Solar Energy
Solar energy is harnessed from sunlight through photovoltaic (PV) panels or solar thermal systems. PV panels convert sunlight directly into electricity, while solar thermal technology uses sunlight to heat water or air for residential and commercial use. This renewable energy source is particularly advantageous because it is clean energy and requires minimal maintenance once installed. The scalability of solar power makes it suitable for both small-scale residential use and large utility-scale projects. For example, solar energy can power homes, charge electric vehicles, or even supply entire cities through solar farms.
Wind Energy
Wind energy is generated by converting the kinetic energy of wind into electricity using wind turbines. This renewable energy source is highly efficient in regions with consistent wind patterns, such as coastal areas or high-altitude zones. Wind farms, whether onshore or offshore, can produce significant amounts of power while occupying relatively small land areas. However, wind energy requires careful planning to minimize its impact on local ecosystems and wildlife, such as birds and bats. Despite these challenges, advancements in turbine technology have made wind energy a reliable and cost-effective option.
Hydropower
Hydropower is one of the oldest and most established renewable energy sources. It relies on the movement of water, typically through dams or run-of-the-river systems, to generate electricity. Hydropower provides a steady and predictable energy supply, making it a cornerstone of renewable energy infrastructure. While large-scale hydropower projects can alter river ecosystems and displace communities, smaller, more sustainable alternatives like micro-hydro systems are gaining popularity. These systems have a lesser environmental footprint and can be integrated into existing waterways without major disruptions.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s internal heat, which is generated by the radioactive decay of minerals in the planet’s core. This renewable energy source is ideal for regions with geothermal activity, such as volcanic areas or tectonic plates. Geothermal power plants can provide both electricity and direct heating for buildings, offering a stable and reliable energy option. Unlike solar or wind, geothermal energy is not affected by weather conditions, making it a dependable choice for baseload power generation. However, its geographical limitations mean it’s not universally applicable.
Biomass Energy
Biomass energy is derived from organic materials such as wood, agricultural crops, and waste from plants and animals. This renewable energy source can be converted into electricity, heat, or biofuels through processes like combustion, gasification, or anaerobic digestion. Biomass energy is particularly useful for rural areas where traditional energy infrastructure is limited. However, its sustainability depends on the source of the biomass and how it’s managed. For instance, using waste products rather than cutting down forests ensures that biomass energy remains a truly renewable option.
The Benefits of Renewable Energy
Adopting renewable energy sources offers a multitude of benefits that extend beyond environmental protection. From reducing greenhouse gas emissions to creating jobs and saving money, the advantages are both immediate and long-term. Let’s delve into the key renewable energy sources and how they can positively impact the planet and society.
Environmental Advantages
One of the most significant benefits of renewable energy sources is their clean energy profile. Unlike fossil fuels, which release carbon dioxide and other pollutants into the atmosphere, renewables produce little to no emissions during operation. For example, solar energy and wind energy generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, helping to reduce carbon footprint and mitigate climate change. Additionally, hydropower and geothermal energy have minimal land use requirements and do not produce air pollution. This guide to renewable energy sources underscores how these options can protect ecosystems and preserve natural resources for future generations.
Economic Benefits
The shift to renewable energy sources also brings substantial economic advantages. The renewable energy sector is a major driver of job creation, from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and research. For instance, the solar industry employs millions of people worldwide, providing opportunities in engineering, sales, and customer service. Moreover, renewable energy sources often have lower operating costs compared to fossil fuels. Once a solar energy system or wind energy turbine is installed, the cost of generating electricity is significantly reduced. This guide to renewable energy sources highlights how these cost savings can benefit both individuals and businesses in the long run.

Social Impact
Beyond environmental and economic gains, renewable energy sources play a vital role in improving social well-being. Access to clean energy can enhance the quality of life for communities, especially in remote or underserved areas. For example, hydropower can provide reliable electricity to rural regions, enabling better education, healthcare, and economic opportunities. Similarly, biomass energy can support local agriculture by utilizing farm waste to generate power. This guide to renewable energy sources emphasizes how these technologies can promote equity and inclusivity in energy access.
Energy Independence
Another key benefit of renewable energy sources is the potential for energy independence. By reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels, countries can enhance their energy security and protect themselves from volatile global markets. For instance, wind energy and solar energy can be harnessed locally, ensuring a steady supply of power regardless of geopolitical tensions. This guide to renewable energy sources also addresses how energy independence can lead to greater resilience and self-sufficiency for communities and nations alike.
How to Transition to Renewable Energy
Transitioning to renewable energy sources requires a strategic approach, whether you’re an individual, a business, or a government entity. This guide to renewable energy sources outlines practical steps to make the shift easier and more effective.
Individual Actions
For individuals, the first step in embracing renewable energy sources is to assess energy usage and identify areas for improvement. Simple changes like using energy-efficient appliances, insulating homes, and switching to clean energy providers can make a significant difference. Additionally, installing solar energy panels or choosing wind energy-powered services are viable options for reducing reliance on fossil fuels. For example, solar energy systems can be tailored to fit different budgets and energy needs, making them accessible to a wide range of consumers.
Business Strategies
Businesses can also play a crucial role in the transition to renewable energy sources. One effective strategy is to invest in on-site renewable energy generation, such as hydropower or geothermal energy, to reduce energy costs and carbon emissions. Another approach is to partner with renewable energy providers and purchase green energy through renewable energy certificates (RECs). Furthermore, companies can integrate biomass energy into their operations by utilizing waste materials for power generation. This guide to renewable energy sources provides actionable insights for businesses looking to adopt sustainable practices.
Government Role
Governments have a pivotal role in accelerating the adoption of renewable energy sources. Policy frameworks, such as subsidies, tax incentives, and renewable energy mandates, can encourage investment in clean energy technologies. For instance, solar energy programs in some countries have led to a dramatic increase in installations by making it financially attractive for homeowners and businesses. Additionally, governments can invest in research and development to improve the efficiency and affordability of renewable energy sources. This guide to renewable energy sources also emphasizes the importance of international cooperation in scaling up renewable energy solutions.
Community Initiatives
Local communities can drive the transition to renewable energy sources by organizing collective efforts and advocating for change. Community solar projects, for example, allow residents to share the benefits of solar energy without the need for individual installations. Similarly, wind energy cooperatives enable communities to invest in wind farms and profit from clean energy production. By fostering collaboration and education, communities can create a supportive environment for renewable energy adoption. This guide to renewable energy sources encourages readers to explore these grassroots initiatives and contribute to a more sustainable future.
The Future of Renewable Energy
As technology continues to advance, the potential of renewable energy sources is expanding rapidly. Innovations in energy storage, smart grids, and hybrid systems are addressing some of the challenges associated with intermittent sources like solar energy and wind energy. For example, geothermal energy is becoming more efficient with new drilling techniques, while biomass energy is evolving with improved biofuel technologies. These developments ensure that renewable energy sources will play an even greater role in shaping the future of energy.
Overcoming Challenges
Despite their benefits, renewable energy sources face challenges such as upfront costs, infrastructure requirements, and geographical limitations. However, these obstacles are increasingly being overcome through technological advancements and policy support. For instance, the cost of solar energy has dropped dramatically in recent years, making it more affordable for households and businesses. Similarly, wind energy is becoming more efficient and reliable with the development of larger turbines and better materials. This guide to renewable energy sources highlights how these innovations are making clean energy more accessible and viable for a wider audience.
Global Collaboration
The transition to renewable energy sources is a global effort that requires collaboration across sectors and nations. International agreements, such as the Paris Climate Accord, have set ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and increasing the share of renewables in the energy mix. Additionally, cross-border partnerships in hydropower and geothermal energy can help countries share knowledge and resources. This guide to renewable energy sources underscores the importance of unity in the fight against climate change and the role of renewable energy in achieving a sustainable world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this guide to renewable energy sources has provided a thorough overview of the key renewable energy sources and their potential to transform the way we generate and consume energy. From solar energy and wind energy to hydropower, geothermal energy, and biomass energy, each option offers unique advantages that can be tailored to specific needs and environments. By understanding these renewable energy sources, individuals, businesses, and governments can take meaningful steps toward reducing their environmental impact and building a more sustainable future.
The benefits of adopting renewable energy sources are clear: they reduce carbon emissions, save money, and promote energy independence. Whether you’re looking to make small changes in your home or invest in large-scale energy solutions, the path to renewable energy is both accessible and impactful. As the world continues to prioritize clean energy and green energy initiatives, the importance of this guide to renewable energy sources cannot be overstated. With the right strategies and collective effort, we can ensure a greener, cleaner, and more resilient world for future generations.