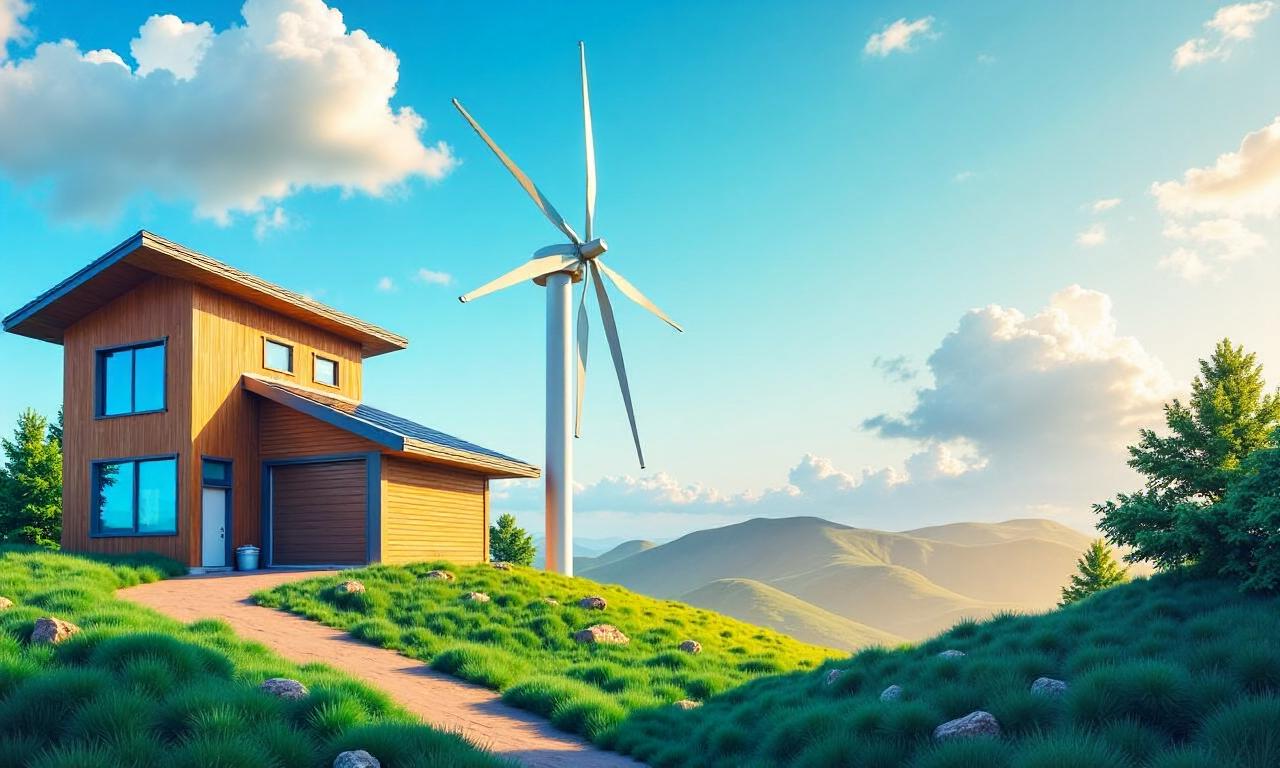
In today’s world, the shift towards sustainable energy is more critical than ever. As global demand for power continues to rise and environmental concerns become increasingly urgent, renewable energy sources have emerged as a cornerstone of the transition to a greener future. This guide to renewable energy sources aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the most viable and impactful options available today. Whether you’re a homeowner looking to reduce your carbon footprint, a business owner seeking energy independence, or simply curious about the future of power generation, this article will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions. The Importance of Renewable Energy Renewable energy is not just a trend; it’s a necessity. Fossil fuels, while still dominant in energy production, come with significant drawbacks such as greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and resource depletion. By contrast, renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower harness natural processes that are both sustainable and inexhaustible. These sources play a vital role in combating climate change, reducing reliance on finite resources, and fostering energy security. The transition to renewables also brings economic benefits. For instance, the renewable energy sector has created millions of jobs worldwide, from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and research. Additionally, renewable energy systems can significantly lower energy costs in the long term, especially as technology advances and economies of scale improve. In this guide to renewable energy sources, we’ll break down the key types, their advantages, and how to choose the best one for your needs. Top Renewable Energy Sources: A Breakdown Renewable energy sources can be categorized into several major types, each with unique characteristics and applications. Understanding these options is essential for anyone looking to adopt sustainable energy practices. Below, we’ll explore the most prominent renewable energy sources and their role in shaping a cleaner energy landscape. Solar Energy: Harnessing the Sun’s Power Solar energy is one of the most accessible and widely used renewable energy sources. It relies on photovoltaic (PV) panels or solar thermal systems to convert sunlight into electricity or heat. The scalability of solar power makes it suitable for both small-scale applications, such as residential rooftops, and large-scale projects, like solar farms. One of the key advantages of solar energy is its abundance. The sun provides more energy in one hour than the entire world consumes in a year. Additionally, solar technology has become more affordable and efficient over the years, with cost reductions making it a competitive option. However, its reliance on sunlight means it can be intermittent, requiring energy storage solutions like batteries to ensure consistent power supply. Wind Energy: Capturing the Power of the Wind Wind energy is another leading renewable energy source, utilizing wind turbines to convert kinetic energy from the wind into electricity. This form of energy is particularly effective in regions with consistent wind patterns, such as coastal areas or open plains. The wind energy sector has seen remarkable growth, driven by advancements in turbine technology and declining costs. Modern wind turbines are more efficient, with larger blades and taller towers allowing them to capture energy from lower wind speeds. Moreover, wind farms can be located offshore, minimizing land use conflicts and maximizing energy output. Despite its benefits, wind energy faces challenges like noise pollution and visual impact, which require careful planning and community engagement. Hydropower: The Power of Water Hydropower has long been a reliable renewable energy source, leveraging the energy of flowing water to generate electricity. This method is particularly effective in areas with rivers or dams, making it a staple in many countries’ energy portfolios. The hydropower industry is known for its consistency and ability to provide baseload power, meaning it can supply energy continuously without interruption. However, large-scale hydropower projects can disrupt local ecosystems and affect water flow, raising concerns about environmental impact. To mitigate these issues, smaller-scale solutions like micro-hydro systems and run-of-the-river projects are gaining popularity. These alternatives reduce the footprint while still delivering clean energy. Geothermal Energy: Tapping into Earth’s Heat Geothermal energy is a unique renewable energy source that harnesses heat from the Earth’s interior. This energy can be used for electricity generation, heating, and even cooling systems. Unlike solar or wind, geothermal energy is available 24/7, making it a reliable option for baseload power. The geothermal energy industry operates by tapping into underground reservoirs of steam and hot water. This process is efficient and produces minimal emissions, as it relies on natural heat rather than combustion. However, geothermal energy is location-dependent, requiring access to geothermal resources, which may limit its applicability in certain regions. Despite this, geothermal energy remains a key player in the renewable energy mix, particularly in countries like Iceland and the United States. Emerging and Alternative Renewable Sources While solar, wind, hydropower, and geothermal are the most established renewable energy sources, there are also emerging technologies and alternative methods that are gaining traction. These innovations are crucial for diversifying the energy mix and addressing specific challenges. Biomass Energy: Power from Organic Matter Biomass energy is a renewable energy source that utilizes organic materials such as wood, agricultural crops, and waste to produce heat or electricity. This method is particularly useful for rural areas or regions with significant organic waste. The process of converting biomass into energy involves combustion or biochemical conversion, such as fermentation. While biomass energy is renewable, it requires careful management to ensure that it doesn’t lead to deforestation or compete with food production. However, advancements in technology have improved efficiency and reduced emissions, making it a more sustainable option. Tidal Energy: Harnessing Ocean Currents Tidal energy is a renewable energy source that captures the kinetic energy of ocean tides to generate electricity. This method is highly predictable, as tides are driven by the gravitational pull of the moon, making it a reliable alternative to other renewables. Although tidal energy is still in its early stages, it holds great potential for coastal regions. Technologies like tidal turbines and underwater generators are being developed to harness this power effectively. However,
Top Energy Saving Gadgets to Cut Your Bills and Save the Planet
In an era where energy costs are rising and environmental concerns are becoming more urgent, energy saving gadgets have emerged as a practical solution for both reducing household expenses and contributing to a sustainable future. From smart home devices to efficient lighting systems, these innovations are designed to minimize energy consumption without compromising comfort or functionality. Whether you’re looking to cut down on your electricity bill or make a meaningful impact on the planet’s energy footprint, investing in the right energy saving gadgets can make a world of difference. This article explores the top energy saving gadgets that are not only cost-effective but also environmentally friendly, helping you save money and energy in your daily life. The Growing Need for Energy Efficiency As global energy demand continues to soar, the need for energy saving gadgets has never been more pressing. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), residential energy use accounts for nearly 30% of total energy consumption worldwide, with heating, cooling, and lighting being the largest contributors. By integrating energy saving gadgets into your home, you can significantly reduce this consumption. These devices leverage smart technology, automation, and advanced energy management systems to optimize efficiency. For instance, energy saving gadgets like smart thermostats and LED lighting systems can lower energy usage by up to 30% in some cases. The benefits of adopting these gadgets extend beyond just financial savings. They also help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which are a major driver of climate change. For example, using energy-efficient appliances can decrease the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere. Additionally, energy saving gadgets often come with features that allow users to monitor their energy consumption in real time, empowering them to make informed decisions about their usage. Smart Thermostats: The Ultimate Energy Monitor What Are Smart Thermostats? Smart thermostats are one of the most popular energy saving gadgets that can transform how you manage heating and cooling in your home. These devices are equipped with advanced sensors and connectivity features that allow them to learn your preferences, adjust temperatures automatically, and even integrate with your home’s other smart systems. Unlike traditional thermostats, which require manual adjustments, smart thermostats use algorithms to optimize energy use based on your habits and external conditions. How They Save Energy Smart thermostats can reduce energy consumption by up to 20% by minimizing the use of heating and cooling systems when they’re not needed. For example, they can detect when you leave the house and automatically switch to energy-saving mode, or adjust the temperature to a more efficient setting while you’re asleep. Some models even use energy saving gadgets like geofencing to ensure your home is only heated or cooled when you’re present. This not only cuts down on utility costs but also reduces the strain on power grids, contributing to a more sustainable energy future. Real-World Impact A study by the U.S. Department of Energy found that using a smart thermostat can save an average of $180 per year on heating and cooling bills. By energy saving gadgets that make your home more efficient, you’re not only saving money but also reducing your carbon footprint. For instance, adjusting the thermostat by just a few degrees can result in significant energy savings over time. Whether you’re using a smart thermostat for temperature control or monitoring energy usage through a mobile app, the long-term benefits are clear. LED Lighting: Brighter and More Efficient The Case for LED Bulbs Lighting accounts for a considerable portion of residential energy use, but LED lighting has revolutionized the market by offering a far more efficient alternative to traditional incandescent and fluorescent bulbs. Energy saving gadgets like LED bulbs consume up to 80% less energy than conventional lighting while providing the same or better light output. Their longevity and low energy consumption make them a must-have for eco-conscious households. How LED Lighting Reduces Energy Waste LED bulbs are designed to convert most of the energy they consume into light, rather than heat, which is a common issue with older technologies. This means you can illuminate your home with less power, leading to substantial energy savings. Additionally, energy saving gadgets such as motion sensors and smart dimmers can be paired with LED lighting to further minimize electricity use. For example, motion sensors ensure lights are only on when needed, reducing unnecessary energy consumption. Environmental and Economic Benefits Switching to LED lighting is a simple yet impactful step toward sustainability. Not only do these bulbs last up to 25 times longer than traditional ones, but they also reduce the need for frequent replacements, cutting down on waste. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), replacing all traditional bulbs with LEDs could save over 348 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity annually. This is equivalent to the energy used by 38 million homes. By using energy saving gadgets like LED lighting, you’re directly contributing to the reduction of energy waste and lowering your utility bills. Energy-Efficient Appliances: Powering Your Home Smartly The Role of Energy Star Appliances Energy efficient appliances are another category of energy saving gadgets that have become essential in modern households. These appliances, often labeled with the Energy Star certification, meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the EPA and the Department of Energy. From refrigerators to washing machines, Energy Star appliances use advanced technology to minimize energy consumption while maintaining performance. How Energy-Efficient Appliances Cut Costs Modern energy saving gadgets like refrigerators and dishwashers are designed to operate with minimal power. For example, an Energy Star certified refrigerator uses about 15% less energy than a non-certified model, which can lead to hundreds of dollars in savings over its lifetime. Similarly, energy-efficient washing machines and dryers can reduce water and electricity use by up to 50%, depending on the model. By choosing energy saving gadgets that are built to last and operate efficiently, you can enjoy long-term savings without sacrificing convenience. The Environmental Impact Beyond cost savings, energy saving gadgets such as energy-efficient appliances also have a positive environmental impact.
Effective Energy Conservation Techniques for a Sustainable Future
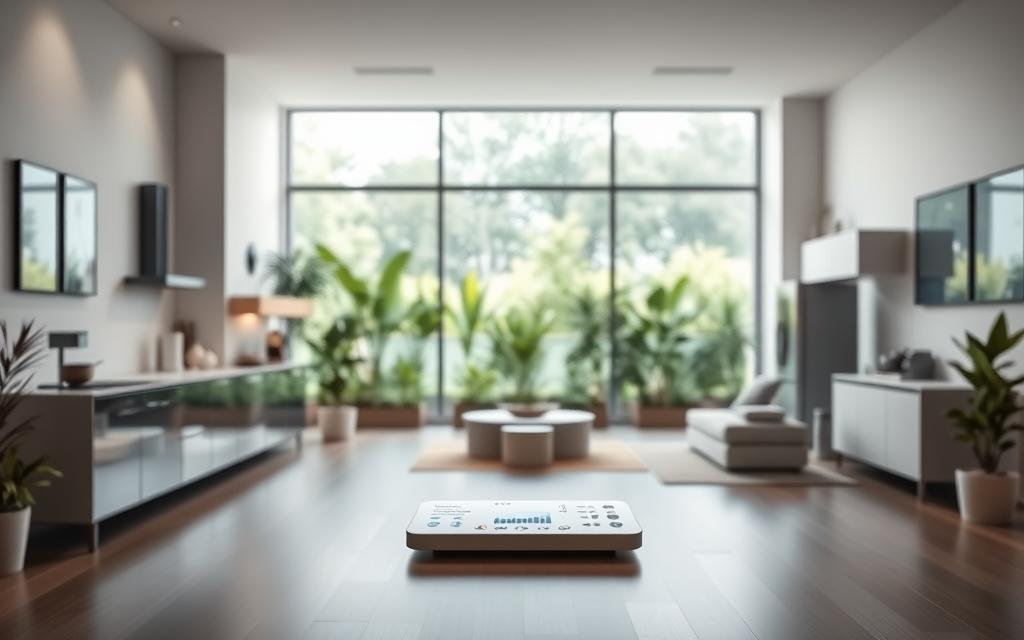
In an era where climate change and resource depletion are pressing global challenges, energy conservation techniques have become more critical than ever. As the demand for energy continues to rise, the need for energy conservation techniques that reduce consumption without compromising quality of life is essential. From individual households to large-scale industries, implementing these energy conservation techniques can significantly lower carbon footprints, reduce energy bills, and promote long-term environmental sustainability. This article explores various energy conservation techniques that are both practical and impactful, helping individuals and organizations contribute to a healthier planet. The Importance of Energy Conservation Techniques in Modern Society Energy conservation techniques are not just about saving money; they are a cornerstone of sustainable development. The global energy sector accounts for a large portion of greenhouse gas emissions, which are the primary contributors to climate change. By adopting effective energy conservation techniques, we can mitigate these emissions, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and preserve natural resources for future generations. Environmental Impact of Energy Consumption The energy conservation techniques we use today directly influence the health of our environment. For instance, energy conservation techniques in residential and commercial sectors can reduce the demand for electricity, which in turn decreases the need for power generation from coal, oil, or natural gas. This reduction helps lower air pollution, water contamination, and the overall ecological footprint. Additionally, conserving energy reduces the extraction of raw materials, preserving ecosystems and biodiversity. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), energy efficiency improvements could contribute to nearly 40% of the required emissions reductions to meet global climate goals by 2040. This highlights the vital role that energy conservation techniques play in achieving a sustainable future. Economic Benefits of Energy Efficiency Beyond environmental advantages, energy conservation techniques offer substantial economic benefits. By using less energy, individuals and businesses can reduce their utility bills, freeing up resources for other priorities. For example, energy conservation techniques like LED lighting and smart thermostats can cut energy costs by up to 30% in homes and offices. On a larger scale, energy-efficient practices help governments save money on infrastructure development, reduce energy imports, and stabilize energy prices. Investing in <strong>energy conservation techniques</strong> today can lead to long-term financial savings, making it a smart choice for both individuals and organizations. Technological Advancements in Energy Conservation Advancements in technology have made energy conservation techniques more accessible and efficient than ever before. Innovations such as smart grids, energy storage systems, and renewable energy sources like solar and wind power are reshaping how energy is produced and consumed. These technologies not only enhance energy efficiency but also enable real-time monitoring and optimization of energy use. The integration of digital tools and automation in <strong>energy conservation techniques</strong> ensures that energy is used more wisely, reducing waste and improving sustainability outcomes. Key Energy Conservation Techniques for Residential Use Home energy consumption is a major contributor to global energy use, making energy conservation techniques in residential settings a priority. Simple changes in daily habits, combined with modern technology, can lead to significant energy savings. Below are some of the most effective energy conservation techniques for households. Smart Lighting Solutions One of the simplest energy conservation techniques is upgrading to energy-efficient lighting. Traditional incandescent bulbs consume a lot of energy and have a short lifespan, while LED bulbs use up to 80% less energy and last significantly longer. LED lighting is a prime example of a energy conservation techniques that reduces electricity bills and minimizes environmental impact. Additionally, using motion sensors or timers for lights can ensure that energy is only used when necessary, further enhancing efficiency. Heating and cooling systems account for a large share of residential energy use, especially in regions with extreme climates. Implementing energy conservation techniques such as regular maintenance of HVAC systems, sealing windows and doors, and using programmable thermostats can drastically improve energy efficiency. Programmable thermostats are a cost-effective <strong>energy conservation techniques</strong> that automatically adjust temperature settings based on occupancy and time of day, saving energy without sacrificing comfort. Reducing Water Heating Costs Water heating is another energy-intensive process in homes. Using energy conservation techniques like installing low-flow showerheads, insulating hot water pipes, and taking shorter showers can significantly cut down on energy use. Additionally, switching to energy-efficient water heaters powered by solar energy or heat pumps can further reduce consumption. By adopting these <strong>energy conservation techniques</strong>, households can lower their energy bills while contributing to the reduction of carbon emissions. Energy-Efficient Appliances and Devices Modern appliances are designed with energy conservation techniques in mind, such as energy Star ratings and smart power management. Replacing old appliances with energy-efficient models can cut energy use by up to 50%. Energy Star-rated appliances are a great example of how energy conservation techniques can be seamlessly integrated into daily life. These devices not only save energy but also reduce the overall environmental impact of household operations. Energy Conservation Techniques in Industrial and Commercial Settings Industrial and commercial sectors are among the largest energy consumers globally, making energy conservation techniques in these areas crucial for reducing overall energy demand. Implementing these techniques can lead to substantial cost savings and a smaller environmental footprint. Upgrading to Energy-Efficient Machinery Industrial facilities often rely on outdated machinery that consumes excessive energy. Upgrading to energy-efficient machinery and equipment can significantly reduce energy waste. For example, replacing traditional motors with high-efficiency models or using variable frequency drives (VFDs) can optimize energy use in manufacturing processes. The adoption of <strong>energy conservation techniques</strong> like <strong>variable frequency drives</strong> ensures that energy is used only when needed, leading to long-term cost savings and reduced emissions. Implementing Smart Building Management Systems Commercial buildings can benefit from energy conservation techniques such as smart building management systems (BMS). These systems use sensors and automation to monitor and control energy use, adjusting lighting, heating, and cooling based on real-time data. Smart building management systems are a key energy conservation techniques that maximizes efficiency by reducing unnecessary energy consumption. For instance, automated lighting systems can turn off lights in unoccupied rooms,